One might argue that identifying the need for anal gland expression in cats is a simple task, requiring minimal knowledge or expertise. However, this perspective overlooks the potential complications and risks of untreated anal gland problems. This article aims to provide an objective and impersonal overview of the signs, causes, prevention, treatment options, and potential complications of anal gland issues in cats. Learn
how to tell if cat needs glands expressed today, as we highlight the importance of veterinary care in managing cat anal gland problems.
Key Takeaways: How to Tell if Cat Needs Glands Expressed
- Scooting, excessive licking or biting at the rear end, foul odor, and swelling or redness around the anus are common signs that indicate a cat may need their anal glands expressed.
- The frequency of anal gland expression varies based on age, breed, diet, and overall health, but some cats may need their anal glands expressed every 1 to 2 months.
- Professional expression of the anal glands by trained experts offers benefits such as accurate identification of when an expression is needed, proper hygiene protocols to minimize the risk of infections or injuries, and minimizing discomfort for the cat.
- Veterinary care is essential for accurately diagnosing and treating anal gland issues in cats, and regular check-ups help identify potential health problems early on, ensuring prompt treatment.
Signs and Symptoms of Anal Gland Issues in Cats
The signs and symptoms of anal gland issues in cats can vary. However, they may include scooting, excessive licking or biting at the rear end, foul odor, swelling or redness around the anus, and difficulty defecating. It is important to note that these symptoms are not exclusive to anal gland issues and could be caused by other health conditions.
The anus appears clean and free from any discharge or abnormalities in a normal cat. However, if a cat is experiencing anal gland problems, it may exhibit signs such as leaking clear fluid from the anus or having white discharge from their bum. These symptoms should prompt further investigation by a veterinarian to determine if the cat’s anal glands need to be expressed or if there is another underlying issue causing these symptoms.
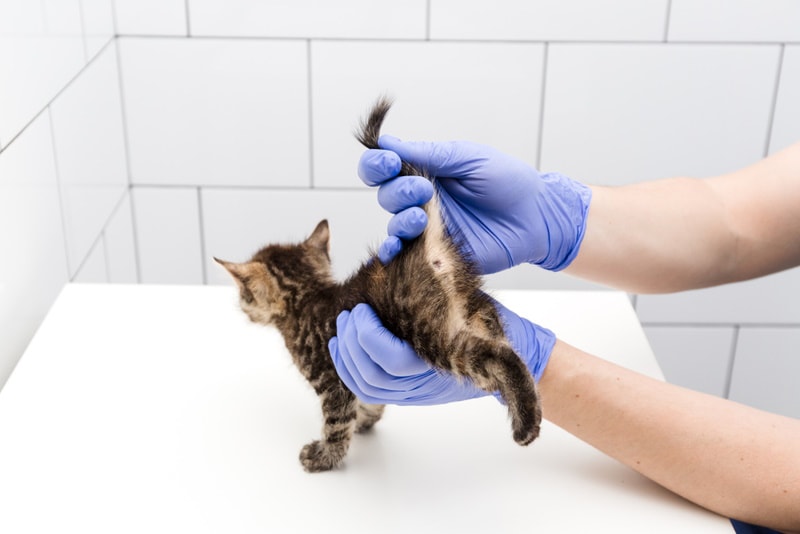
Causes and Prevention of Anal Gland Problems in Cats
This discussion will focus on the benefits of a high-fiber diet and its role in preventing anal gland problems in cats. High-fiber diets have been shown to promote healthy digestion and regulate bowel movements, which can help prevent the buildup of fluid and debris in the anal glands. By maintaining optimal stool consistency, a high-fiber diet reduces the risk of anal gland impaction or infection, ultimately improving the overall well-being of cats.
High-Fiber Diet Benefits
Research has shown that a high-fiber diet can offer various benefits for cats. Fiber is an essential component of a cat’s diet as it aids in maintaining normal bowel movements and promoting digestive health. A high-fiber diet helps to regulate stool consistency, preventing issues such as constipation or diarrhea. Additionally, fiber promotes the growth of beneficial gut bacteria, contributing to overall gastrointestinal health.
A healthy cat butthole is characterized by regular and firm stools, indicating proper digestion and absorption of nutrients. It is important to note that a cat butt hole should not show any signs of discomfort or inflammation, such as redness or swelling. If a cat has clear liquid from its anus, it may indicate an underlying issue requiring veterinary attention. Therefore, incorporating a high-fiber diet into a cat’s nutrition plan can contribute to maintaining a normal kitten butt and ensuring healthy cat buttholes.
Preventing Anal Gland Problems
Preventing anal gland problems requires regular care and attention to the hygiene of a cat’s perianal area. Maintaining a healthy cat anus is crucial in preventing complications associated with anal glands. One common sign of anal gland issues is the presence of white discharge from the cat’s anus. This discharge, sometimes called “white stuff on cats bum,” can indicate an underlying problem with the anal glands that may require veterinary attention.
It is important to note that cats sniff each other’s butts as part of their natural behavior, which helps them gather information about one another. However, if excessive sniffing or discomfort is observed, it could be a sign of anal gland problems. Regular grooming and keeping the perianal area clean can help prevent these issues and ensure the overall well-being of your feline companion.
Treatment Options for Anal Gland Problems in Cats
Treatment options for anal gland problems in cats include manual expression, dietary modifications, and the use of medications. Manual expression is a technique where a veterinarian or trained professional manually squeezes the anal glands to remove any accumulated fluid or debris. This procedure should be performed by someone experienced to prevent injury or infection.
Dietary modifications can help promote regular bowel movements and firm stools, reducing the risk of anal gland problems. Increasing fiber intake through specialized diets or supplements may be recommended. Medications such as antibiotics or anti-inflammatory drugs may be prescribed if an infection or inflammation is present. It’s important to note that any changes in discharge from the cat’s anus, such as white discharge or clear, odorless fluid in male or female cats, should be evaluated by a veterinarian to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment plan.
Potential Complications and Risks of Anal Gland Problems in Cats
Complications and risks associated with anal gland problems in cats may include:
- Abscess formation: Abscesses can form when the anal glands become blocked or infected, leading to pain and discomfort for the cat.
- Recurrent infections: If the anal glands are not properly expressed or an underlying issue causing blockage, recurrent infections can occur, requiring ongoing treatment.
- Anal sacculitis and perianal fistulas: Inflammation of the anal sacs and the development of abnormal passages between them (perianal fistulas) can result from chronic anal gland problems.
- Development of tumors: In some cases, long-standing issues with the anal glands can lead to the growth of tumors.
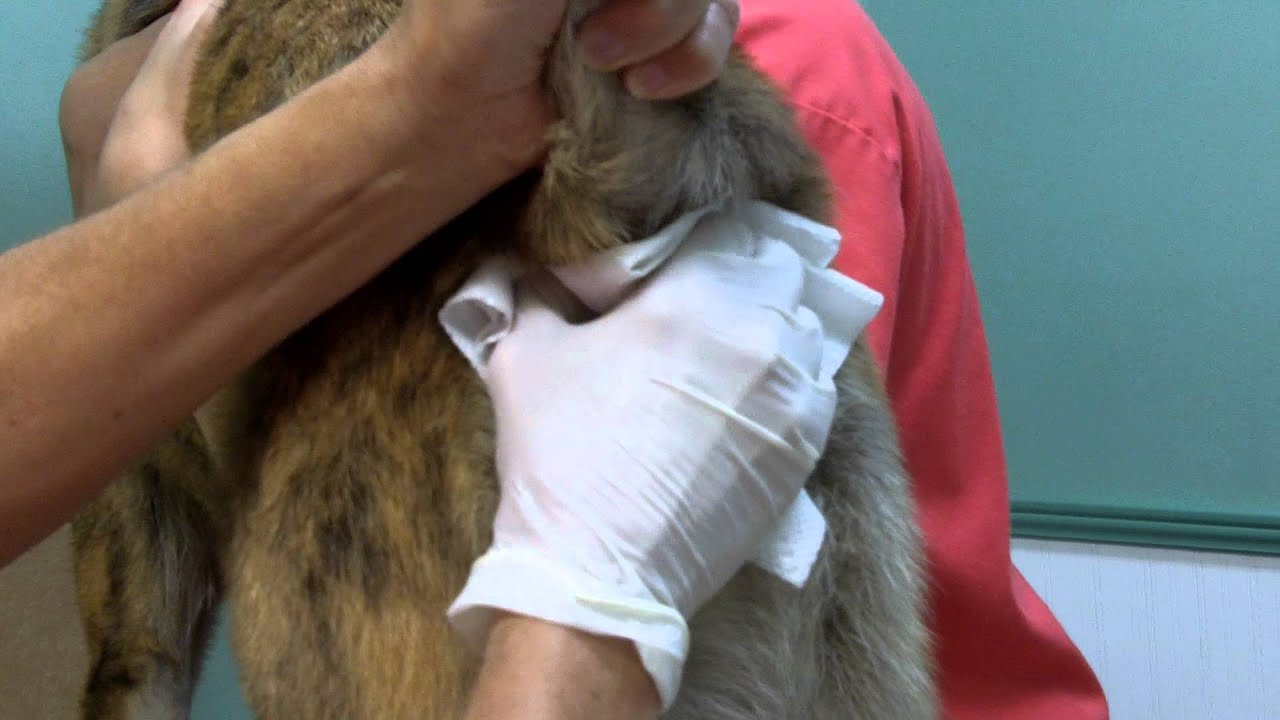
Cat owners must be vigilant and observe any discomfort or abnormal behavior related to their cat’s bottom area. These may include a female cat with white discharge from her anus or a male cat with white creamy discharge from his anus. Additionally, a white smelly discharge from a cat’s anus could indicate an infection or other issue that needs prompt attention. It is also worth noting that cats sniffing each other’s bums is part of their normal social behavior for information gathering.
Expressing Cat’s Anal Glands: How, When, and Where
This discussion aims to explore the techniques and methods used for expressing a cat’s anal glands and the frequency at which this procedure should be performed. Additionally, it will examine the benefits of having a professional perform anal gland expression on cats. By examining these key points, we can better understand how to properly maintain a cat’s anal gland health and prevent potential complications.
Expressing Techniques and Methods
Expressing techniques and methods for cat anal glands involve manual manipulation of the glandular sacs to release the accumulated secretions. This procedure is essential in preventing discomfort and potential health issues for cats. Here are three effective techniques for expressing cat anal glands:
- External Expression: This technique involves applying gentle pressure on either side of the anus to help release the contents of the glands.
- Internal Expression: A veterinarian or trained professional inserts a gloved finger into the rectum to manually manipulate and empty the impacted anal glands.
- Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed to soften the secretions, making it easier for them to empty naturally during bowel movements.
Understanding why cats smell each other’s butts or sniff each other’s bums is linked to their unique communication method. By smelling another cat’s anal area, they can gather important information about their age, gender, reproductive status, and overall health.
Frequency of Expression
Having examined the techniques and methods of expressing a cat’s anal glands, it is now pertinent to shift focus towards understanding the frequency in which this process should occur. Observation plays a key role in determining this frequency. The action of a cat sniffing other cats’ bum or a male cat sniffing a female cat’s bum, for instance, can be indicative of an issue. Understanding why do cats smell each others bums may help identify discomfort or anomalies that necessitate glandular expression. A question often asked by feline owners; ‘why does my cat sniff my other cats bum?’ could potentially indicate the need for more frequent expressions. Therefore, monitoring these behaviors closely contributes significantly to maintaining optimal feline health.
Benefits of Professional Expression
Professional gland expression offers several advantages, including a reduced risk of injury or infection to the cat’s anal glands. This procedure is performed by trained professionals with the expertise and knowledge to handle cats safely and effectively. The benefits of professional gland expression include:
- Expertise: Trained professionals are skilled in accurately identifying when a cat’s glands need to be expressed, ensuring the procedure is done correctly.
- Safety: Professionals follow proper hygiene protocols and use sterile techniques, minimizing the risk of infections or injuries during gland expression.
- Comfort: Professional expression techniques are designed to minimize discomfort for the cat, ensuring a less stressful experience.
These advantages make professional gland expression a reliable option for addressing issues related to anal gland problems in cats.
Signs of Cat Anal Gland Issues: What to Look Out For
This discussion examines the common signs and symptoms of cat anal gland issues, explores the various treatment options available, and highlights the importance of seeking veterinary care. Recognizing the signs of anal gland problems in cats is crucial for early intervention and appropriate management.
Treatment options may include manual expression, dietary changes, medication, or even surgical intervention, depending on the severity of the condition. Veterinary care is essential to accurately diagnose and effectively treat cat anal gland issues while ensuring the overall health and well-being of the animal.
Common Signs and Symptoms
Common signs and symptoms of the need for cat gland expression include:
- scooting, excessive licking or biting of the anal area,
- foul odor,
- swelling or redness around the anus, and
- discomfort during bowel movements.
These indicators can be distressing to both cats and their owners. It is crucial to address these issues promptly to prevent further complications.
It is important to consider their natural instincts to understand why cats exhibit certain behaviors related to their anal glands. Cats have a highly developed sense of smell and communication through scent marking. Sniffing each other’s bottoms allows them to gather information about one another, such as identifying individuals, detecting pheromones, or establishing social hierarchies.
Moreover, cats rely on their sense of smell to recognize family members or detect potential environmental threats. This ability helps them determine whether they are familiar with another cat or should approach it cautiously.
Sometimes, a white creamy discharge from a male cat’s anus may indicate an infection or blockage that requires veterinary attention. Understanding these behaviors can help you provide appropriate care for your feline companion when necessary.
Treatment Options Available
Treatment options are available for cats that need to have their glands expressed. If a cat shows signs such as leaking clear fluid or having a white substance coming out of its anus, it may indicate the need for gland expression. This procedure can be performed by a veterinarian or a trained professional who understands the anatomy and process involved.
The treatment involves manually emptying the anal glands to relieve discomfort or potential infection. It is important to note that if a cat’s anus appears red, swollen, or has an abnormal color, it should be evaluated by a veterinarian to rule out any underlying conditions. In some cases, dietary changes may also be recommended to help prevent future issues with the anal glands.
Importance of Veterinary Care
The importance of veterinary care for cats experiencing symptoms such as leaking clear fluid or a white substance from the anus lies in accurately diagnosing and addressing any underlying conditions causing these issues. Regular veterinary check-ups can help identify potential health problems early on, ensuring prompt treatment and preventing further complications. Here are some reasons why seeking veterinary care is crucial:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Veterinary professionals have the knowledge and expertise to perform thorough examinations and diagnostic tests to determine the cause of your cat’s symptoms.
- Tailored Treatment: Once the underlying condition is identified, veterinarians can develop a customized treatment plan based on your cat’s needs and requirements.
- Preventative Measures: Veterinary care addresses existing issues and focuses on preventive measures to maintain your cat’s overall health and well-being.
Importance of Veterinary Care for Cat Anal Gland Problems
The importance of veterinary care for cat anal gland problems cannot be understated. Cats have a unique way of communicating, often involving sniffing each other’s bums. This behavior may seem strange to humans, but it serves an important purpose in the feline world. By smelling another cat’s bum, they can gather information about its health and status. In some cases, cats may develop issues with their anal glands, leading to discomfort and infection.
Pet owners must understand the signs that indicate their cat needs its glands expressed. These signs include scooting or dragging their bottom along the floor, excessive licking or biting at the area, and foul odors. Seeking veterinary care promptly is essential to address any anal gland problems and ensure the well-being of our feline companions.

